Navigating Conflicts of Interest in the Review Writing Industry
Ever found yourself questioning the neutrality of a glowing product review? Surprisingly, 85% of consumers rely on reviews before making a purchase, only to be misled at times by hidden biases.
This blog post shines a light on spotting and managing those tricky conflicts of interest in review writing. Keep reading; it gets clearer from here!
Key Takeaways
- A conflict of interest in review writing occurs when a reviewer’s personal or financial interests might influence their evaluation, potentially leading to biased results.
- Reviewers must declare all possible conflicts of interest, such as owning company stock or having personal ties with authors, before starting the review process to maintain trust and impartiality.
- Transparency is key; disclosing funding sources and any related financial or non – financial interests helps readers judge the credibility of reviews and ensures ethical standards are upheld.
- Non – financial conflicts like personal relationships, professional biases, ideological views, academic recognition desires, or career advancement goals can also affect research objectivity and must be disclosed.
- Interviewing experts in the field can help identify hidden biases while developing clear disclosure statements bolsters transparency and reinforces confidence in the research findings.
Understanding Conflicts of Interest in Research
Conflicts of interest in research can arise from financial or non-financial interests that may bias the results or conclusions of a study. It is important for researchers to disclose any potential conflicts of interest to maintain transparency and credibility in their work.
Definition of conflict of interest
A conflict of interest in review writing arises when a reviewer’s personal interests could potentially influence their judgment or integrity. This can happen if the reviewer has financial interests, such as owning stock in a company whose product they’re reviewing, or non-financial ties like close relationships with the authors of the work under consideration.
The key concern is that these interests may sway the evaluation process, either consciously or subconsciously, leading to biased outcomes.
Managing conflicts of interest requires honesty and transparency. Reviewers must declare all potential conflicting interests before assessing a manuscript to maintain impartiality in review writing.
It’s vital for upholding ethical standards and ensuring that reviews are conducted without undue influence from private gains or external pressures. Ethical guidelines for reviewers insist on disclosure to prevent any appearance of impropriety and safeguard the credibility and integrity of both the review process and published research.
Importance of disclosing conflicts of interest
Disclosing conflicts of interest ensures integrity in review writing. It’s a crucial step toward maintaining trust between researchers, peer reviewers, and the public. When authors and reviewers declare their financial interests or personal connections related to their work, they uphold ethical standards.
This transparency helps readers assess the credibility of findings and recommendations.
Effective conflict of interest management prevents bias from swaying outcomes or interpretations in research. Reviewers who reveal any potential competing interests demonstrate commitment to impartiality in review writing.
Such openness is fundamental to advancing knowledge while protecting academic honesty and the value of published works.
Types of Conflicts of Interest
Financial conflicts of interest can arise when a researcher has a financial stake in the outcome of the study. On the other hand, non-financial conflicts of interest could include personal relationships or academic competition that may influence the review process.
Understanding different types of conflicts is crucial for maintaining integrity in research writing.
Financial conflicts of interest
Money can influence a person’s decisions, and that’s why financial conflicts of interest are critical to identify in review writing. Researchers must be vigilant and transparent to maintain integrity.
Non-financial conflicts of interest
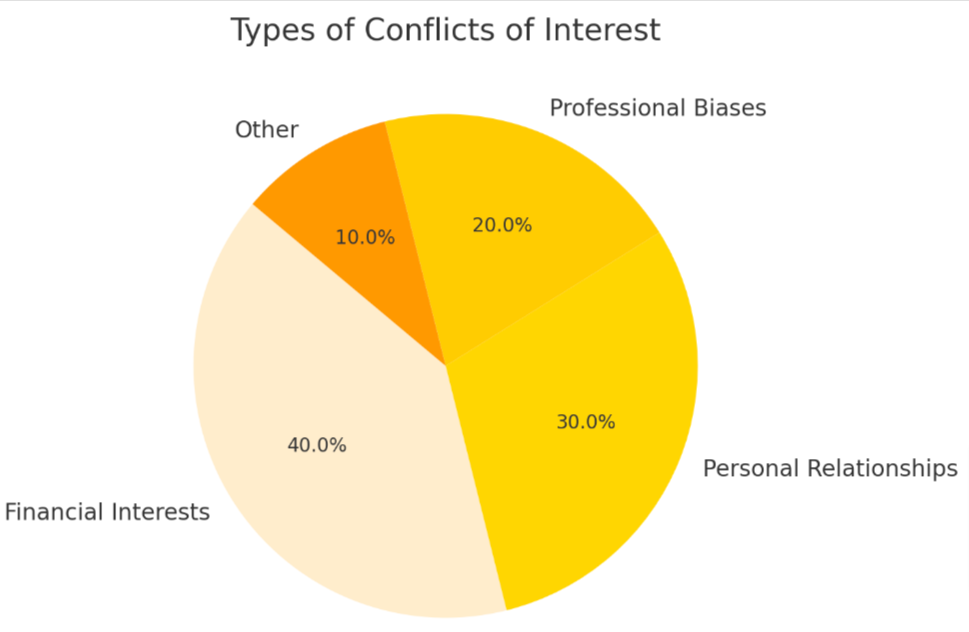
Non-financial conflicts of interest arise from personal, professional, or academic relationships that may influence research objectivity. These can include intellectual passion for a particular idea, personal beliefs, or career advancement aspirations.
- Personal Relationships: Connections with individuals or organizations involved in the research can impact impartiality.
- Professional Bias: Academic collaborations or mentor-mentee relationships may lead to unconscious bias in the review process.
- Ideological Considerations: Strong advocacy for specific viewpoints or theories could sway judgment.
- Academic Recognition: Pursuit of recognition and prestige within the scientific community might compromise impartiality.
- Career Advancement: Ambitions for tenure, funding, or promotions could affect decision-making in review writing.
Sponsorship of clinical trials
When it comes to conflicts of interest in research, sponsorship of clinical trials is a significant area that requires careful consideration. Sponsors of clinical trials may have vested interests in the outcome, potentially impacting the objectivity and integrity of the research findings.
Transparency about sponsorships is crucial to maintaining the credibility and reliability of clinical trial results. Researchers need to be diligent in disclosing any affiliations with sponsors and ensuring that their findings are not unduly influenced by these relationships.
Involvement with sponsored clinical trials can introduce bias into the research process, making it essential for reviewers and researchers to approach such studies with heightened scrutiny.
How to Address Conflicts of Interest in Research Writing
Declare conflicts of interest in manuscripts and conduct interviews with experts to identify potential biases. Develop clear disclosure statements and ensure transparency in research funding to maintain ethical standards in review writing.
Declaring conflicts of interest in manuscripts
To declare conflicts of interest in manuscripts, researchers should:
- Clearly state any financial interests related to the research topic, such as stock ownership or consulting fees.
- Disclose any non – financial conflicts of interest that could potentially bias their review, such as personal relationships with individuals involved in the research.
- Provide transparent information about sponsorship of clinical trials and other funding sources that may influence the research findings.
- Include a detailed disclosure statement outlining all potential conflicts of interest to ensure transparency and maintain ethical guidelines.
- Interview experts in the field to gain insights into potential biases and ensure impartiality in the review process.
Interviews with experts
Experts in the field of research ethics and conflict of interest guidelines share valuable insights. These interviews provide practical tips for identifying, managing, and disclosing conflicts of interest in review writing.
Through these discussions with experts, reviewers can gain a deeper understanding of ethical responsibilities, ensuring transparency in their research funding, and promoting impartiality in their review writing process.
Conducting interviews with experts is an essential part of gaining comprehensive knowledge about handling conflicts of interest in review writing. The guidance provided by these experts helps reviewers navigate through ethical considerations effectively and maintain integrity throughout the review process.
Developing clear disclosure statements
Developing clear disclosure statements helps in transparently communicating any potential conflicts of interest to readers. It ensures ethical considerations and instills confidence in the integrity of the research. Here are key steps in developing clear disclosure statements:
- Clearly state any financial ties to organizations related to the research.
- Disclose any personal relationships or professional connections that could create bias.
- Explain any funding sources for the research and how they may influence the findings.
- Detail any previous collaborations with individuals or organizations related to the study.
- Provide a comprehensive overview of all potential conflicts of interest related to the review writing.
Ensuring transparency in research funding
Researchers must ensure transparency in research funding by disclosing all sources of financial support for their work. Clear and comprehensive disclosure statements should be developed to outline any potential conflicts of interest related to the funding.
Additionally, interviews with experts can provide valuable insight into managing conflicts of interest and ensuring ethical guidelines are met throughout the research process.
Moving forward, it is crucial to understand the types of conflicts of interest that can arise during research writing and how to address them effectively. By identifying potential bias and managing conflicts of interest, researchers can maintain impartiality and integrity in their review writing.
Conclusion
In handling conflicts of interest in review writing, it’s crucial to disclose any potential biases. Reviewers should declare financial and non-financial interests in their manuscripts.
Ensuring transparency in research funding is essential for maintaining ethical standards. Managing conflicts of interest requires developing clear disclosure statements and conducting interviews with experts.
Maintaining integrity and impartiality is vital for unbiased and transparent review writing.

